期货和现货补偿
原文: https://www.backtrader.com/docu/order-creation-execution/futurespot/future-vs-spot/
发布版1.9.32.116增加了对社区中呈现的有趣用例的支持
-
开始与期货交易,包括实物交割
-
让指示器告诉你一些事情
-
如果需要,通过现货价格操作平仓,有效地取消实物交割,无论是收货还是必须交割(并有望获利)
期货在现货价格操作发生的同一天到期
这意味着:
-
该平台由来自两种不同资产的数据点提供
-
平台必须以某种方式理解资产之间的关联,并且在现货价格上的操作将关闭期货上未平仓的头寸
现实中,未来不是封闭的,只有实物交付补偿
使用补偿概念,backtrader增加了一种方式,让用户与平台沟通,一个数据馈送上的东西会对另一个产生补偿效果。使用模式
import backtrader as bt
cerebro = bt.Cerebro()
data0 = bt.feeds.MyFavouriteDataFeed(dataname='futurename')
cerebro.adddata(data0)
data1 = bt.feeds.MyFavouriteDataFeed(dataname='spotname')
data1.compensate(data0) # let the system know ops on data1 affect data0
cerebro.adddata(data1)
...
cerebro.run()
把它们放在一起
一个例子总是值一千篇文章,所以让我们把所有的部分放在一起。
-
使用
backtrader来源的标准样品进料之一。这将是未来 -
模拟一个相似但不同的价格,通过重复使用相同的提要并添加一个过滤器,该过滤器将随机将价格移动到上/下一些点,以创建价差。简单到:
```py
The filter which changes the close price
def close_changer(data, args, *kwargs): data.close[0] += 50.0 * random.randint(-1, 1) return False # length of stream is unchanged ```
-
在同一轴上绘图将混合默认包含的
BuyObserver标记,因此标准观察者将被禁用并手动读取,以使用不同的 per 数据标记进行绘图 -
职位将随机输入,10 天后退出
这与未来的到期期限不匹配,但这只是将功能落实到位,而不是检查交易日历
!!! 笔记
A simulation including execution on the spot price on the day of
future expiration would require activating `cheat-on-close` to
make sure the orders are executed when the future expires. This is
not needed in this sample, because the expiration is being chosen
at random.
-
请注意,该策略
-
buy操作在data0上执行 -
sell操作在data1上执行
```py class St(bt.Strategy): def init(self): bt.obs.BuySell(self.data0, barplot=True) # done here for BuySellArrows(self.data1, barplot=True) # different markers per data
def next(self): if not self.position: if random.randint(0, 1): self.buy(data=self.data0) self.entered = len(self) else: # in the market if (len(self) - self.entered) >= 10: self.sell(data=self.data1)```
-
执行:
$ ./future-spot.py --no-comp
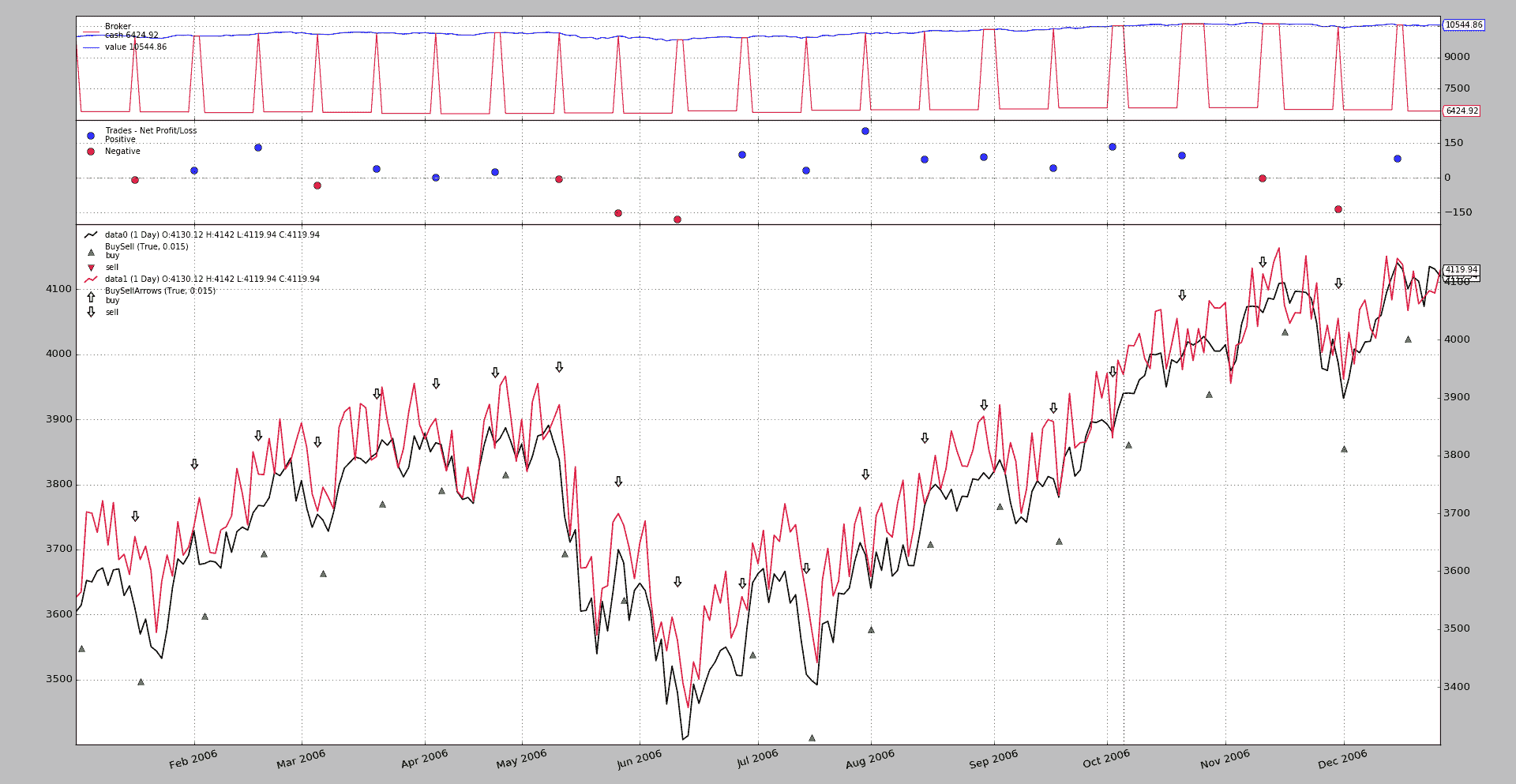
使用此图形输出。
它的工作原理是:
-
buy操作用一个指向上方的绿色三角形表示,图例告诉我们它们属于data0,正如预期的那样 -
sell操作用一个向下的箭头表示,图例告诉我们它们属于data1,正如预期的那样 -
交易正在关闭,即使它们是以
data0打开并以data1关闭,也达到了预期效果(在现实生活中,这是避免通过未来获得的货物的实物交付)
人们只能想象,如果在不进行补偿的情况下应用相同的逻辑会发生什么。让我们开始吧:
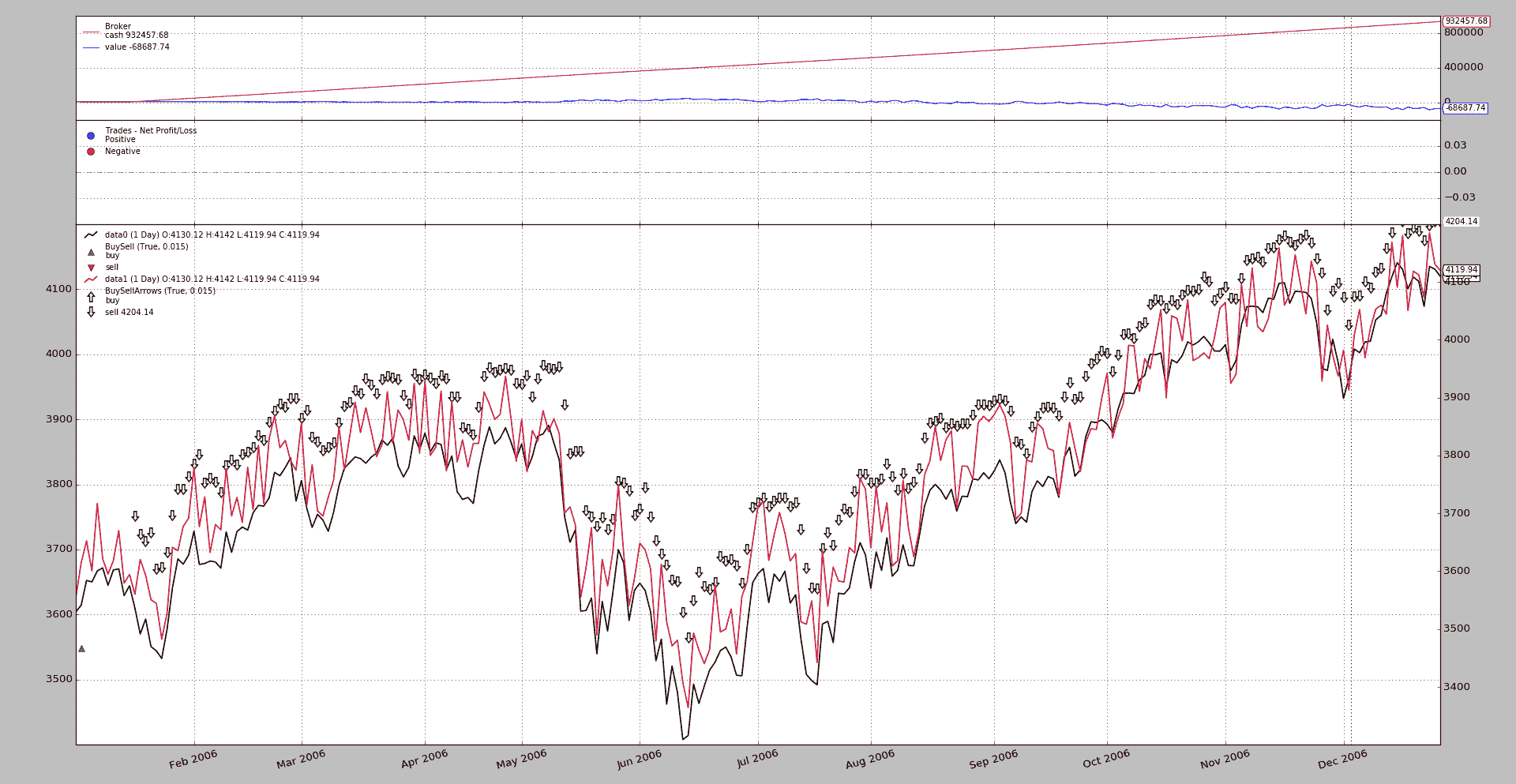
$ ./future-spot.py --no-comp
以及输出
很明显,这一点失败得很惨:
-
该逻辑预计
data0上的头寸将通过data1上的操作关闭,并且只有data0上的头寸在不在市场上时才会打开 -
但补偿已停用,且
data0(绿色三角形)上的初始操作从未关闭,因此无法启动其他操作,data1上的空头头寸开始累积。
样本使用
$ ./future-spot.py --help
usage: future-spot.py [-h] [--no-comp]
Compensation example
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--no-comp
示例代码
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function,
unicode_literals)
import argparse
import random
import backtrader as bt
# The filter which changes the close price
def close_changer(data, *args, **kwargs):
data.close[0] += 50.0 * random.randint(-1, 1)
return False # length of stream is unchanged
# override the standard markers
class BuySellArrows(bt.observers.BuySell):
plotlines = dict(buy=dict(marker='$\u21E7$', markersize=12.0),
sell=dict(marker='$\u21E9$', markersize=12.0))
class St(bt.Strategy):
def __init__(self):
bt.obs.BuySell(self.data0, barplot=True) # done here for
BuySellArrows(self.data1, barplot=True) # different markers per data
def next(self):
if not self.position:
if random.randint(0, 1):
self.buy(data=self.data0)
self.entered = len(self)
else: # in the market
if (len(self) - self.entered) >= 10:
self.sell(data=self.data1)
def runstrat(args=None):
args = parse_args(args)
cerebro = bt.Cerebro()
dataname = '../../datas/2006-day-001.txt' # data feed
data0 = bt.feeds.BacktraderCSVData(dataname=dataname, name='data0')
cerebro.adddata(data0)
data1 = bt.feeds.BacktraderCSVData(dataname=dataname, name='data1')
data1.addfilter(close_changer)
if not args.no_comp:
data1.compensate(data0)
data1.plotinfo.plotmaster = data0
cerebro.adddata(data1)
cerebro.addstrategy(St) # sample strategy
cerebro.addobserver(bt.obs.Broker) # removed below with stdstats=False
cerebro.addobserver(bt.obs.Trades) # removed below with stdstats=False
cerebro.broker.set_coc(True)
cerebro.run(stdstats=False) # execute
cerebro.plot(volume=False) # and plot
def parse_args(pargs=None):
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
description=('Compensation example'))
parser.add_argument('--no-comp', required=False, action='store_true')
return parser.parse_args(pargs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
runstrat()