轴心点与交会图
笔记
保留这一职位是出于历史原因。指示器和样本已经在源代码中更新,PivotPoint现在可以自动耦合,删除用户代码的样板文件。
一篇新的文章将引用这篇文章。同时,请查看来源中的更新样本。
遇到了一个有趣的请求:
- 支点
这很有趣,因为指标是如何定义的。文献可在股票图表的支点处找到。数据透视点使用过去时间段的close、high和low价格。例如,对于每日时间框架:
- 日线图的轴心点使用上月数据
这似乎很麻烦,因为对于每个时间段,都需要定义必须使用的其他时间段。查看这些公式会发现另一个问题:
Pivot Point (P) = (High + Low + Close)/3
Support 1 (S1) = (P x 2) - High
Support 2 (S2) = P - (High - Low)
Resistance 1 (R1) = (P x 2) - Low
Resistance 2 (R2) = P + (High - Low)
即使文本中充满了对前期和过去的引用,公式似乎也引用了当前时间点。让我们按照文本的建议,在第一次尝试使用之前的作为支点。但首先,让我们通过这样做来解决不同时间段的问题:
- 该指标无法解决这一问题
尽管这似乎令人困惑,但我们必须考虑到指标必须尽可能愚蠢,并由实际公式组成。问题将按以下方式解决:
data = btfeeds.ADataFeed(..., timeframe=bt.TimeFrame.Days)
cerebro.adddata(data)
cerebro.resampledata(data, timeframe=bt.TimeFrame.Months)
后来在策略中:
class MyStrategy(bt.Strategy):
def __init__(self):
self.pp = PivotPoint(self.data1) # the resampled data
现在清楚了。该系统将有数据,加上额外的输入重新采样到所需的时间范围。而PivotPoint指标将与重新采样的数据一起工作,该数据已经在原始数据时间段日所需的月时间段内。
可以开发该指标。让我们从文本指示开始,而不是公式,然后回顾一段时间。
class PivotPoint1(bt.Indicator):
lines = ('p', 's1', 's2', 'r1', 'r2',)
def __init__(self):
h = self.data.high(-1) # previous high
l = self.data.low(-1) # previous low
c = self.data.close(-1) # previous close
self.lines.p = p = (h + l + c) / 3.0
p2 = p * 2.0
self.lines.s1 = p2 - h # (p x 2) - high
self.lines.r1 = p2 - l # (p x 2) - low
hilo = h - l
self.lines.s2 = p - hilo # p - (high - low)
self.lines.r2 = p + hilo # p + (high - low)
策略将查看参数usepp1以使用此PivotPoint1
def __init__(self):
if self.p.usepp1:
self.pp = PivotPoint1(self.data1)
else:
self.pp = PivotPoint(self.data1)
输出由一个简单的next方法控制
def next(self):
txt = ','.join(
['%04d' % len(self),
'%04d' % len(self.data0),
'%04d' % len(self.data1),
self.data.datetime.date(0).isoformat(),
'%.2f' % self.pp[0]])
print(txt)
让我们执行:
./ppsample --usepp1
以及输出:
0041,0041,0002,2005-02-28,2962.79
0042,0042,0002,2005-03-01,2962.79
...
立刻有一件事很清楚:指数 41 已经属于第 2个月。这意味着我们跳过了 1 个月的指标计算。现在很清楚为什么股票图表中的文字总是提到计算发生在前月,但公式似乎引用了当前时刻。
-
开发人员可能面临相同的设计决策,使用多个时间段的多个数据。
在当前日点,只有上一月的关闭条可以发货。
这就是为什么next方法要查看索引[0]。所有这些都有一个非常简单的解决方案,那就是编写公式,就像股票图表记录它们一样。
class PivotPoint(bt.Indicator):
lines = ('p', 's1', 's2', 'r1', 'r2',)
plotinfo = dict(subplot=False)
def __init__(self):
h = self.data.high # current high
l = self.data.low # current high
c = self.data.close # current high
self.lines.p = p = (h + l + c) / 3.0
p2 = p * 2.0
self.lines.s1 = p2 - h # (p x 2) - high
self.lines.r1 = p2 - l # (p x 2) - low
hilo = h - l
self.lines.s2 = p - hilo # p - (high - low)
self.lines.r2 = p + hilo # p + (high - low)
没有usepp1的执行:
./ppsample
新的输出是:
0021,0021,0001,2005-01-31,2962.79
0022,0022,0001,2005-02-01,2962.79
...
瞧!第 1st个月有20个交易日,完成后指标已计算出数值并可交付。唯一打印的行是p,如果两行中的值相同,是因为该值在整个下个月内保持不变。引用股票图表:
Once Pivot Points are set, they do not change and remain in play throughout ...
指示器已经可以使用了。让我们开始策划吧。已设置打印参数
plotinfo = dict(subplot=False)
计算值与数据刻度一致,就像移动平均值一样,可以沿着数据绘制(因此subplot=False)
与--plot一起执行:
./ppsample --plot
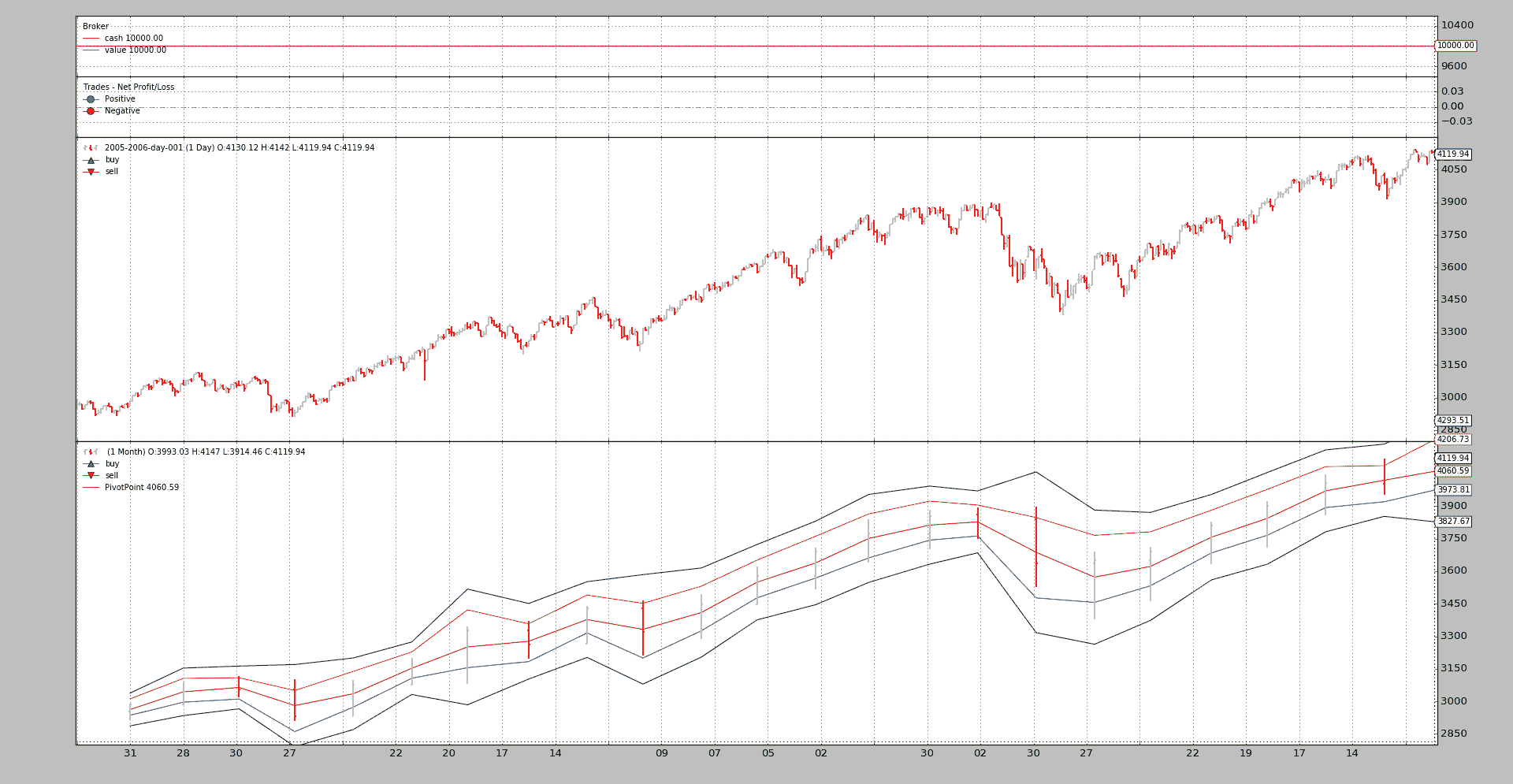
起泡的藤壶又开始攻击了。该指标已绘制在月度数据(其来源)上,在日线图上没有给出直观的指示,这将非常有用。
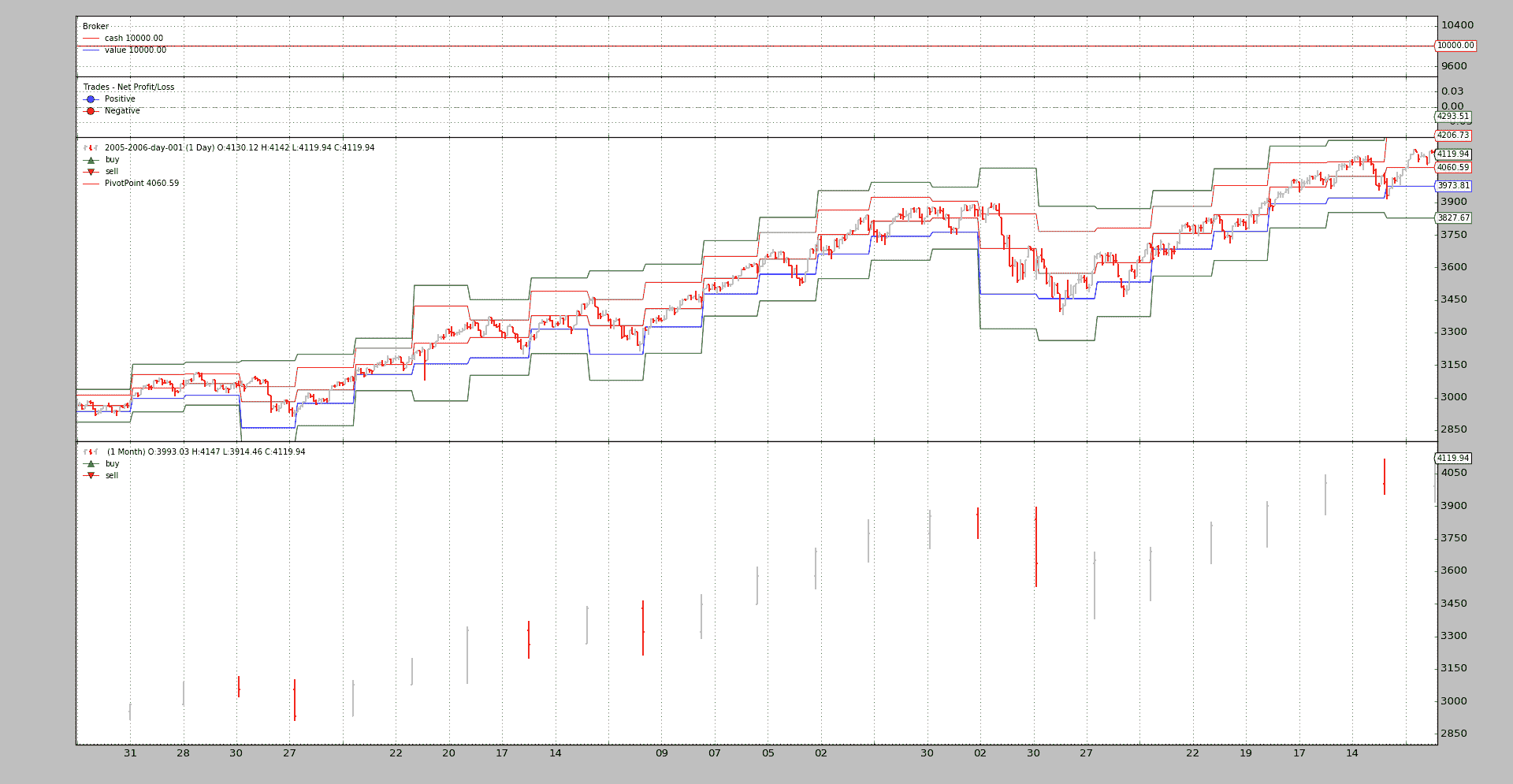
但backtrader支持从一个数据到另一个数据的交叉绘制。虽然需要在1.2.8.88中添加一个小的内容,以支持对不同时间段的数据进行交叉绘制。
这是通过将plotmaster添加到指示器的plotinfo属性中,让plotmaster说出绘图目标是什么来实现的:
./ppsample --plot --plot-on-daily
视觉反馈现在有助于理解PivotPoint提供了什么。
脚本代码和用法
可在backtrader来源中作为样本获得:
$ ./ppsample.py --help
usage: ppsample.py [-h] [--data DATA] [--usepp1] [--plot] [--plot-on-daily]
Sample for pivot point and cross plotting
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--data DATA Data to be read in (default:
../../datas/2005-2006-day-001.txt)
--usepp1 Have PivotPoint look 1 period backwards (default: False)
--plot Plot the result (default: False)
--plot-on-daily Plot the indicator on the daily data (default: False)
PivotPoint的代码
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function,)
# unicode_literals)
import backtrader as bt
class PivotPoint1(bt.Indicator):
lines = ('p', 's1', 's2', 'r1', 'r2',)
def __init__(self):
h = self.data.high(-1) # previous high
l = self.data.low(-1) # previous low
c = self.data.close(-1) # previous close
self.lines.p = p = (h + l + c) / 3.0
p2 = p * 2.0
self.lines.s1 = p2 - h # (p x 2) - high
self.lines.r1 = p2 - l # (p x 2) - low
hilo = h - l
self.lines.s2 = p - hilo # p - (high - low)
self.lines.r2 = p + hilo # p + (high - low)
class PivotPoint(bt.Indicator):
lines = ('p', 's1', 's2', 'r1', 'r2',)
plotinfo = dict(subplot=False)
def __init__(self):
h = self.data.high # current high
l = self.data.low # current high
c = self.data.close # current high
self.lines.p = p = (h + l + c) / 3.0
p2 = p * 2.0
self.lines.s1 = p2 - h # (p x 2) - high
self.lines.r1 = p2 - l # (p x 2) - low
hilo = h - l
self.lines.s2 = p - hilo # p - (high - low)
self.lines.r2 = p + hilo # p + (high - low)
脚本的代码。
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function,
unicode_literals)
import argparse
import backtrader as bt
import backtrader.feeds as btfeeds
import backtrader.utils.flushfile
from pivotpoint import PivotPoint, PivotPoint1
class St(bt.Strategy):
params = (('usepp1', False),
('plot_on_daily', False))
def __init__(self):
if self.p.usepp1:
self.pp = PivotPoint1(self.data1)
else:
self.pp = PivotPoint(self.data1)
if self.p.plot_on_daily:
self.pp.plotinfo.plotmaster = self.data0
def next(self):
txt = ','.join(
['%04d' % len(self),
'%04d' % len(self.data0),
'%04d' % len(self.data1),
self.data.datetime.date(0).isoformat(),
'%.2f' % self.pp[0]])
print(txt)
def runstrat():
args = parse_args()
cerebro = bt.Cerebro()
data = btfeeds.BacktraderCSVData(dataname=args.data)
cerebro.adddata(data)
cerebro.resampledata(data, timeframe=bt.TimeFrame.Months)
cerebro.addstrategy(St,
usepp1=args.usepp1,
plot_on_daily=args.plot_on_daily)
cerebro.run()
if args.plot:
cerebro.plot(style='bar')
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
description='Sample for pivot point and cross plotting')
parser.add_argument('--data', required=False,
default='../../datas/2005-2006-day-001.txt',
help='Data to be read in')
parser.add_argument('--usepp1', required=False, action='store_true',
help='Have PivotPoint look 1 period backwards')
parser.add_argument('--plot', required=False, action='store_true',
help=('Plot the result'))
parser.add_argument('--plot-on-daily', required=False, action='store_true',
help=('Plot the indicator on the daily data'))
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == '__main__':
runstrat()